Oil and Gas Pipeline Monitoring
Leak detection in buried oil and water pipelines:
- using differential thermal imaging
- using Ultra Wideband, or differential RF, sub-surface probing
Ultra Wide Bandwidth (UWB) ground probing RADAR to:
- spot oil leaks
- detect buried metallic objects
Oil and gas pipeline watch
There is increasing legislation and regulatory pressures in the USA to improve the safety and integrity of pipelines carrying hydrocarbons.
In the USA there are 3,476,000 Km of pipelines carrying hydrocarbons.
In Russia there are 0.11 to 0.14 pipeline breaks per Km per year.
A 40" diameter pipeline is designed to carry up to $10 million of hydrocarbons per day.
Catastrophic failures can cause fatalities and massive environmental damage, as in Belgium in 2004, in Nigeria in 2005 and in Prudhoe Bay in 2006.
from Schlumberger posters
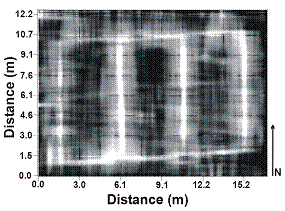
Image from work at Ohio State University, using $20,000 … $25,000 Ground Penetrating RADAR system to locate pipes from 0.7 ...1.2 m below the ground surface with 81% effectiveness.
from http://www.geology.ohio-state.edu/~jeff/Library/ASAE_Geophysics_Paper_1.pdf
Some of the longer oil and gas pipelines throughout the world
The Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline
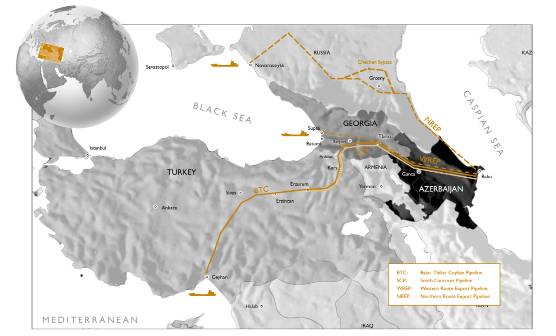
- type = oil pipeline
- cost = £ 1.8 billion
- length = 1,768km
The Trans Alaska Pipeline (TAP) linking Prudhoe Bay to Valdez
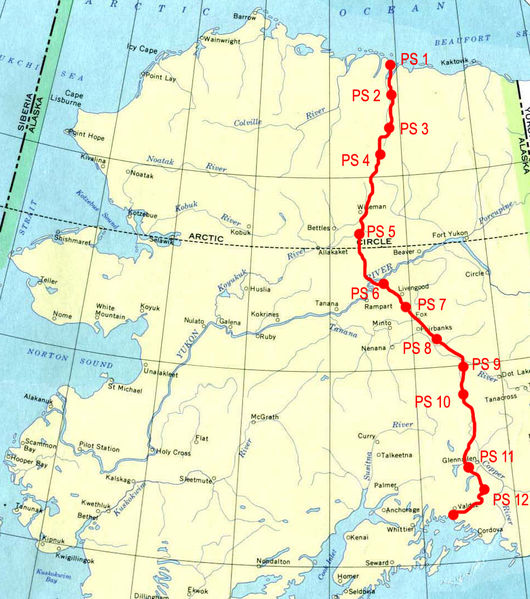
from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Trans_alaska_international.jpg
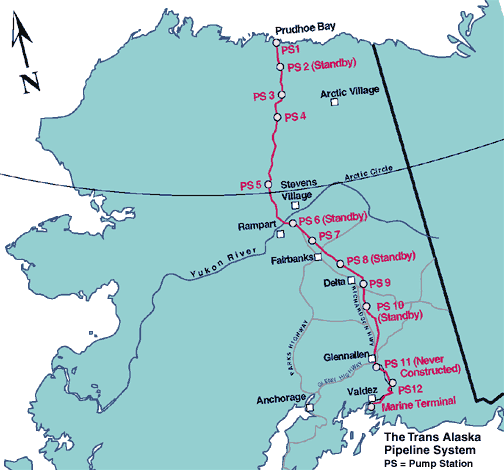
from http://www.d.umn.edu/~hoef0049/pipelinemap.html
- type = oil pipeline carrying at most 2 million barrels per day
- cost = $8 billion
- length = 1,287km (800 miles)
The Turkmenistan - Afganistan - Pakistan (TAP) pipeline with an extension to India (planned)
 pipeline.jpg)
from http://www.ringnebula.com/Oil/Pipeline.htm
- type = natural gas pipeline
- cost = $2.9 billion +$ 0.6 billion for the extension to India
- length = 1,271 Km + 640 Km for the extension to India
How has leakage in oil pipelines been detected?
Prudhoe Bay leakage in March 2006: 267,000 gallons
from http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/11696601/

An emergency worker monitors a vacuum sucking up oil and melted snow on Friday near a pipeline where a leak was discovered a day earlier.
First indication: by SMELL
Chuck Hamel, of Alexandria, Va, said operators knew there was a leak at least 36 hours before the spill was found, because the smell of crude vapors was noted. " They knew they had a problem," he said. " They could smell it, but they couldn't find it." Johnson said the spill was discovered almost immediately after a worker smelled it.
Location: by SOUND
A bubbling sound helped workers pinpoint a leak in a pipeline that allowed thousands of gallons of crude oil to spill onto the frozen tundra in Alaska's Prudhoe Bay.
The breach was discovered at 1:40 a.m. Sunday inside a low-lying section of the 34-inch transit line, which leads to the trans-Alaska oil pipeline. The section where the leak occurred is covered by gravel to let caribou pass.
"All kinds of technology has been brought to the North Slope, and the way it was actually found was that someone heard a gurgling noise, put some lights on it, and saw it," Maureen Johnson, BP manager of the Prudhoe Bay unit, said during a briefing with reporters.
The source of the leak was found after enough snow had been removed from the site. The spill, discovered Thursday by a BP operator, prompted the company to shut down the processing plant, depressurize the line and block off both ends, but workers Sunday found that oil is still dripping from the breach.
Crews have worked under considerable challenges, including temperatures dipping to 20 degrees below zero and deep snow hiding much of the spill. The leak was difficult to detect because oil can seep into insulation and the sheath surrounding the line, exiting at a distance.
Installed leak detection systems
The installed leak detection systems for the Trans Alaskan Pipeline (left column) and the Sakhalin II Pipeline Transportation System (right column).
| Leak detection | Leak alert systems, number 4. Leak alert systems, types - Pressure deviation, flow rate deviation, flow rate balance and line volume balance. | Under design, but will be statistical mass balance system to detect leaks less than 1% of flow rate. |
from http://www.sakhalinenergy.com/en/index.wbp
The Aerostar UAV in oil and gas pipeline monitoring
from https://aeronautics-sys.com/
Pipeline Monitoring & Oil and Gas Security
Offshore oil & gas installations are extremely valuable assets, situated across extensive maritime areas that are difficult to guard. Attacks or damage to such installations can lead to enormous ecological damage, revenue losses and chaos on international oil markets. Improving oil and gas security security is a matter of global importance.
UAVs are today emerging as highly effective tools for confronting pipeline monitoring, and oil and gas security challenges. While others have speculated about the possible use of UAVs in offshore oil security, Aeronautics has put theory into practice, becoming a world pioneer in this field.

Oil and Gas Security – UAV Systems
For over three years, since 2003, the Company’s Aerostar Tactical UAVs have been patrolling offshore oil fields on a regular basis. Even at night, the Aerostar’s FLIR camera reveals the presence of thieves and potential kidnappers, who often try to reach the rigs using small boats. Oil leaks and slicks also show up clearly in infrared, and by detecting them early Aerostar has saved oil companies millions in fines, which are imposed automatically for such leaks.
The Aerostar’s flight profile, with its 12 hours endurance, slow loitering speed and fully programmable flight path, make it ideal for this surveillance role. Aerostar can remain in the air the whole night long and inspect each rig thoroughly. Using manned aircraft for this role is impractical, because the frequent maintenance required to support so many flight hours would be extremely costly and time consuming, and the inevitable boredom involved would raise dangers for the pilot.

Pipeline Monitoring – UAV Systems
Another critical role for the UAV is the infrared inspection of the thousands of miles of pipelines that transport oil and gas around the world. Oil and gas leaks show up well in infrared because of the temperature differences between the fluid and the soil. Undetected leaks have frequently caused disastrous fires, explosions and loss of life, as well as heavy economic losses. Again, the UAV is the best and most economical type of platform for this inspection work.